Bonds
1. Bonds ?
A bond is a debt instrument issued for a predetermined period of time with the purpose of raising capital by borrowing. A bond generally involves a promise to repay the principal and interest on specified dates. This kind of debt instrument may also be called as bills or notes and these names are used interchangeably in the market. Bond is not a fixed deposit. If the investment period of time is the same, the return from bonds are relatively higher than fixed deposit.
There are many different kinds of bonds. The common ones are: fixed rate bond, floating rate bond, zero coupon bond and certificate of deposit, etc.
For enquiries, please call our customer service hotline (852) 2287 8965.
2.What are the common features of bonds?
Principal
• Also called the par value or face value. It is the amount to repay bondholders at the maturity date of bonds?
Coupon Rate
• The interest rate which bond issuer pays annually. Interest payments can be made at regular intervals of annually, semi-annually or quarterly
• The coupon rate of fixed rate bonds is fixed at the issue date
• The coupon rate of floating rate bonds will be reset periodically (usually once every 3 months). It will be based on the then referred market rates plus a spread. The interest spread is determined at the bond issue date
Maturity Date
• The date when bond issuer pays back the principal in full
• If maturity date is not set, it is regarded as perpetual bond
Residual Maturity
• The remaining time before maturity date
• The longer the residual maturity, the easier the bond price will be affected by market rates
Credit Rating
• The credit rating of bonds tells us about the credit quality. It means the financial ability of bond issuer to pay interest on schedule and repay the principal at maturity
• The higher the rating, the lower the risk. However, the yield will be relatively lower as well
Bond Price
• The prices quoted in the secondary market where investors can buy/sell bonds at
• Bond prices are quoted in percentage of the face value
Settlement Arrangement
• Settlement date usually varies from T+3 to T+5
Bond Yield
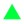
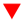
• Bond yield means the rate of return on bonds
• Yield to maturity is the most common term used for bond yield. It assumes you hold bonds until the maturity date and reinvest all interest payments received with the same rate of return
• Bond yield and bond price are in inverse relation
| Bond Yield | Bond Price |
 |
 |
 |
 |
3.Types of Bonds?
(A) Bonds can be categorized by capital tiers. It represents the seniority of claims in case of a default event.
Senior /Subordinated Debt
• Senior debt refers to creditors have a priority of claim over subordinated debt and equity on issuer’s assets in the event of liquidation. Senior debt usually includes funds borrowed from banks or other financial institutions and creditors. Specific deposits not covered by government/industry protection scheme are also common to have senior debt ranking.
• Subordinated debt refers to its investors are placed in a lien position behind or subordinated to senior debt investors. The interest payments and principal of securities issued as subordinated debt will be paid only after the creditors of senior debt got paid in the case of bankruptcy or liquidation.
• To compensate the higher risk subordinated debt investors need to take, the yield of subordinated debt is generally higher than that of senior debt. But remember, it is just another example of high risk, high return.
Secured /Unsecured Debt
• Secured debt refers to debt obligation backed by certain assets or revenue of the borrower. In the event of default, creditors of secured debt can force sell such assets to fulfill their claims.
• Unsecured debt refers to debt obligation not backed by any of the borrower’s assets for the event of bankruptcy or liquidation. The senior debts in the market are mainly unsecured debts.
• In light of this, secured debts are not necessarily more secured.
On the other hand, bonds can also be categorized by different types of maturity:
Bullet Bond
• Principal will be repaid at a fixed maturity date.
Callable Bond
• Issuer has an option of redeeming the bond at a predetermined call date before maturity.
Perpetual Bond
• A kind of bond without maturity date. Issuer does not set a date for repaying the principal like bullet bond or callable bond. Rather, perpetual bond will keep paying coupon interest to bondholders indefinitely. Most of the perpetual bonds are callable. Issuers can choose to repay the principal at a specific day which is set at the bond issue date.
Copyright@2024 CASH Financial Services Group



